
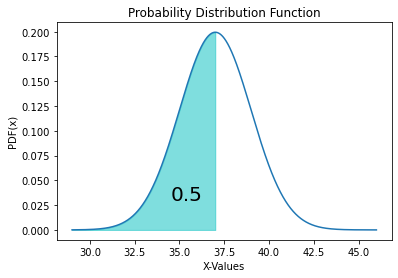
P(a\lt X \lt b) = \displaystyle \int_a^b f(x)dxįor a probability density function to be valid, no probabilities may be negative, and the total probability must be one. In general, the probability that a continuous random variable will be between limits a and b is given by the integral, or the area under a curve.
#Pdf vs cdf pdf
We calculate probabilities based not on sums of discrete values but on integrals of the PDF over a given interval.

It is usually more straightforward to start from the CDF and then to find the PDF by taking the derivative of the CDF. Thus, we should be able to find the CDF and PDF of Y. If X is a continuous random variable and Y g ( X) is a function of X, then Y itself is a random variable. Continuous probability distributions are probability density functions, or PDFs. 4.1.3 Functions of Continuous Random Variables. This document may be reproduced for educational and research purposes, so long as the copies contain this notice and are retained for personal use or distributed free. With a continuous random variable, we care only about the random variable taking on a value in a particular interval. pdf’s, cdf’s, conditional probability Septemc 2013 by Christopher A. Even if we could meaningfully measure the waiting time to the nearest millionth of a second, it is inconceivable that we would ever get exactly 8.192161 seconds. The accuracies of these algorithms are only meant to be sufficient for. Keep in mind that, in most instances, approximations were used to speed up calculations and accommodate the limitations of javascript. However, it makes little sense to find the probability that a car will wait precisely 8.192161 seconds at the light. This page shows the results of various javascript functions used in statistical calculations on this site. If the traffic light has a cycle lasting 30 seconds, then 8.192161 seconds is a possible outcome. The cdf is not discussed in detail until section 2.4 but I feel that introducing it earlier is better. For example, suppose we measure the length of time cars have to wait at an intersection for the green light. The cumulative distribution function (CDF or cdf) of the random variable X has the following definition: F X ( t) P ( X t) The cdf is discussed in the text as well as in the notes but I wanted to point out a few things about this function.

The situation is different for continuous random variables. For example, we might calculate the probability that a roll of three dice would have a sum of 5.
#Pdf vs cdf trial
With discrete random variables, we often calculated the probability that a trial would result in a particular outcome.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
